

NamePolicy=kernel database onboard slot path Systemd-networkd supports MAC address spoofing via link files (see systemd.link(5) for details). Note: A device cannot be in use (connected in any way or with its interface up) while the MAC address is being changed. Where XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX is the MAC you wish to change to.įinally, to return the MAC address to its original, permanent hardware value: # macchanger -mac= XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX interface To change the MAC address to a specific value, you would run: To randomize only device-specific bytes of current MAC address (that is, so that if the MAC address was checked it would still register as being from the same vendor), you would run the command: The MAC address can be spoofed with a fully random address:

The spoofing is done on per-interface basis, specify network interface name as interface in each of the following commands. It provides a variety of features such as changing the address to match a certain vendor or completely randomizing it. If it worked, 'link/ether' should be whatever address you decided to change it to.Īnother method uses macchanger (a.k.a., the GNU MAC Changer).
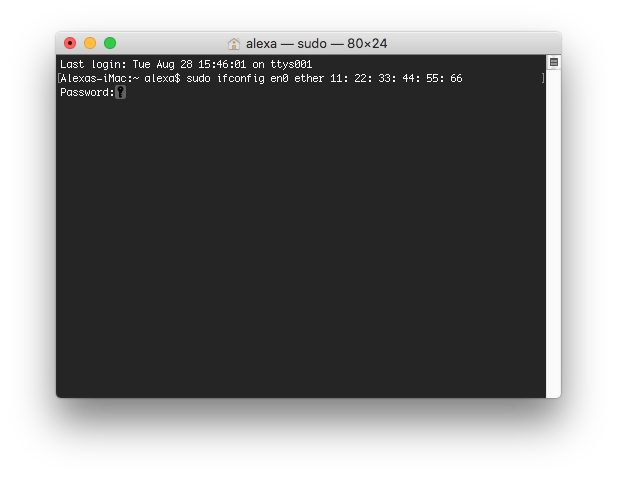
If you want to verify that your MAC has been spoofed, simply run ip link show interface again and check the value for 'link/ether'. This can be accomplished by running the command: The final step is to bring the network interface back up. Where any 6-byte value will suffice for XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX. # ip link set dev interface address XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX To change the MAC, we need to run the command: For more information please read Wikipedia:Organizationally unique identifier. Therefore, unless you control the network(s) you are connecting to, use MAC prefix of any real vendor (basically, the first three bytes), and use random values for next three bytes. Any hexadecimal value will do, but some networks may be configured to refuse to assign IP addresses to a client whose MAC does not match up with any of known vendors. The first step to spoofing the MAC address is to bring the network interface down. It will probably look something like this: The section that interests us at the moment is the one that has "link/ether" followed by a 6-byte number. Where interface is the name of your network interface. Both of them are outlined below.įirst, you can check your current MAC address with the command: There are two methods for spoofing a MAC address: installing and configuring either iproute2 or macchanger. This article gives several methods to spoof a Media Access Control (MAC) address.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
